Ulcers, It's causes, Signs and Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment.
By Rita Soludo
An ulcer is a break or sore in a bodily membrane that impedes normal function of the affected organ.
According to Robin's pathology, ulcer us the breach of the continuity of the skin, epithelium or mucous membrane caused by sloughing out of inflamed necrotic tissue. Common forms of ulcers recognized in medicine include;
1.) Pressure ulcer: Also known as bedsores.
2.) Genital ulcer : An ulcer located in the genital area.
3.) Ulcerative dermatitis: A skin disorder associated with bacterial growth often initiated by self-trauma.
4.) Anal fissure: Also known as an ulcer or tear near the anus or within the rectum.
5.) Diabetic foot ulcer: A major complications of the diabetic foot.
6.) Corneal ulcer: An inflammatory or infective condition of the cornea.
7.) Mouth ulcer: An open sore inside the mouth.
8.) Aphthous ulcer: A specific type of oral ulcer also known as a canker sore.
9.) Peptic ulcer: A discontinuity of the gastrointestinal mucosa(stomach ulcer)
10.) Venous ulcer: An ulcer which occurs due to the improper functioning of the valves of the veins
11.) Stress ulcer: An ulcer located within the stomach and proximal duodenum. It is found in critically ill or intensely stressed patients.
12.) Ulcerative sarcoidosis: A cutaneous condition affecting people with sarcoidosis.
13.) Ulcerative lichen planus: A rare varient of lichen planus.
14.) Ulcerative colitis: A form of inflammatory bowel disease.
15.) Ulcerative disposition : A disorder or discomfort that causes severe abdominal distress often associated with chronic gastritis.
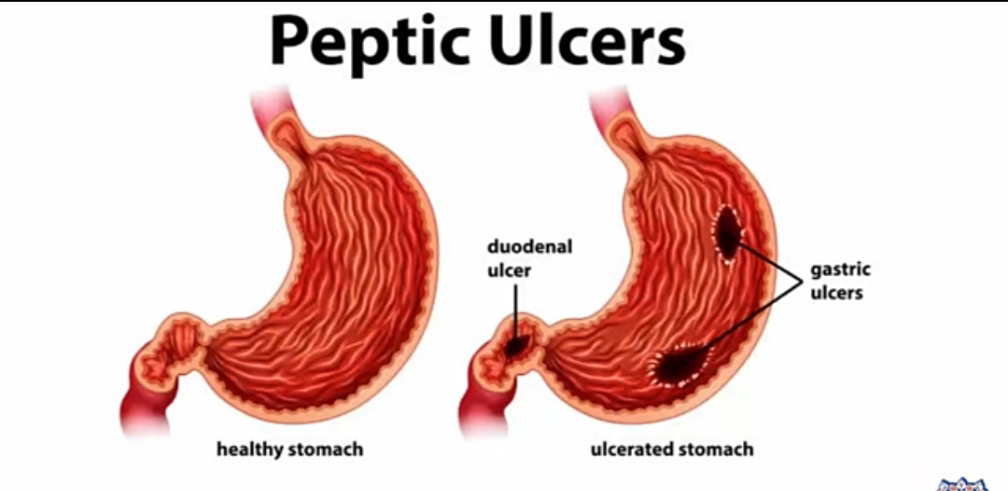
PEPTIC ULCERS
Peptic ulcers are painful sores that are present in the protective lining of the digestive tract. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, oesophagus, stomach, duodenum and the intestine.
Ulcer are relatively easy to treat but can cause problems if left untreated. Peptic ulcers are the most common ulcer type. Peptic ulcers are associated with the presence of pepsin( an enzyme found in the digestive system) along with Hydrochloric acid in the stomach lining.
TYPES
Peptic ulcers are of three(3) types and are named for their location in the body. If the Peptic ulcer is in the stomach it is reffered to as Gastric Ulcer. If the Peptic ulcer is in the duodenum it is reffered to as Duodenal Ulcer. While the peptic ulcer formed in the oesophagus is known as Esophageal Ulcer.
A peptic ulcer that has been left untreated can result to internal bleeding. Internal bleeding is a very critical matter that requires urgent medical attention. This is the most severe of all ulcers and if left unattended to may lead to severe consequences. A refractory ulcer is a term used to refer to an ulcer that has not healed over a period of time.
CAUSES
An ulcer is formed when the mucus layer protecting the tissues of the body against digestive juice (acid) breakdown . This breakdown may be as a result of,
1.) An infection due to helicobacter pylori (a gram negative bacteria found in the digestive system.
2.) Frequent use of NSAID's ( Non- steroidal antiinflammatory drugs) such as Aspirin, ibuprofen and naproxen.
3.) Smoking.
4.) Stomach cancer.
5.) Radiation therapy.
6.) Excessive alcohol intake.
7.) Excessive stomach acid secretion.
SYMPTOMS
. Abdominal pains that starts between meals or at night.
. Discomfort after meals.
. Heartburn.
. Bad breath.
. Constipation.
. Abnormal weight loss.
. Nausea and vomiting.
. Unusual headaches.
. Sleep problems.
. Change in appetite.
. Indigestion.
. Bloody or dark stool.
DIAGNOSIS
Diagnosing ulcer will depend on your symptoms and intensity of the ulcer. Your doctor will request for your medical history to review it and follow up on your symptoms by asking questions about how the pain feels, how frequent it is, how long it lasts and any medications you are taking.
A blood stool or breath test may be ordered to check for infections in your stool caused be helicobacter pylori. In the case of more serious symptoms like bleeding other tests may be required such as;
An Upper endoscopy where a thin tube with a camera is inserted and passed down the oesophagus into your stomach and small intestines to visualize and examine the area for ulcers.
An Upper gastrointestinal test or upper G.I : In this procedure the patient is asked to drink a thick white liquid called barium that coats your upper gastrointestinal tract, making possible for your doctor to view and treat the ulcer on x-rays. This procedure is also referred to as barium swallow.
TREATMENT
The treatment may be surgical or non-surgical depending on the underlying cause of the ulcer.
1.) Non-surgical treatments: If an ulcer is due to helicobacter pylori infections the doctor will prescribe antibiotics to help kill infections and proton pump inhibitors to block acid producing cells. If h.pylori has been ruled out, proton pump inhibitors may be prescribed this with blocking acid producing cells.
Other non-surgical treatments includes stopping all use of NSAID'S .
The use of H2-receptor blockers that reduces acid production, antacids and bismuth supplements are classes of drugs used in the non-surgical treatment of peptic ulcers.
2.) Surgical treatments: In rare cases where the ulcer bleeds, refuses to heal, continues to occur or stops food from leaving the stomach surgical treatments may be required. The surgery may include; removal of the ulcer, tying off the blood vessel or cutting off the nerve that produces acid in the stomach.